Amendments in the FEMA, 1999

RBI Updates January 2024
1. Amendment to Framework for Facilitating Small Value Digital Payments in Offline Mode
- Vide: RBI/2024-25/93/DPSS.POLC.No.S1264/02-14-003/2021-2022
- Dated: December 04, 2024
The RBI circular which facilitated small-value digital payments in offline mode under the Offline Framework has been updated, and enhanced limits for UPI Lite have now been announced, as detailed below:
UPI Lite Limits | Previous Limits | Enhanced Limits |
Transaction Limit | ₹500 per offline digital payment | ₹ 1,000 per transaction |
Total Limit | ₹2,000 for a payment instrument | ₹ 5,000 for a payment instrument |
Effective Date:
The changes are effective immediately from the date of the circular, December 4, 2024.
Link:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/NT93BF202BF7266D4E5FB257B8D6EDA5A686.PDF
2. Support to Agriculture Sector– Collateral-free agricultural loans
- Vide: RBI/2024-2025/96/ FIDD.CO.FSD.BC.No.10/05.05.010/2024-25
- Dated: December 06, 2024
- The RBI decided to raise the limit for collateral-free agricultural loans including loans for allied activities from the existing level of ₹1.6 lakh to ₹2 lakh per borrower.
- Accordingly, banks were advised to waive collateral security and margin requirements for agricultural loans including loans for allied activities upto ₹2 lakh per borrower.
This is a critical step in empowering rural communities and fostering economic inclusivity. Increased rural credit limits will benefit companies focused on rural markets.
The link to the aforesaid Circular is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/NOT96144E24E148514F10B93A2E1CD4D649B1.PDF
3. Maintenance of Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- Vide: RBI/2024-25/95/DoR.RET.REC.52/12.01.001/2024-25
- Dated: December 06, 2024
Background on Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is a regulatory requirement for commercial banks in India, mandated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It refers to the percentage of a bank’s total net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) that must be maintained as reserves in the form of cash with the RBI. The primary purpose of CRR is to ensure the liquidity and solvency of banks. It helps the RBI control the money supply and maintain stability in the financial system.
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) Reduced to 4%
In a significant move to enhance liquidity, the RBI slashed the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) by 50 basis points. This will inject ₹1.16 lakh crore into the banking system, supporting credit growth and financial stability.
Key Point | Details |
Notification Date | December 06, 2024 |
Legal Framework | Notification made under the Reserve Bank Act, 1934 and the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 |
Current CRR Reduction | Reduction of CRR by 50 basis points in two tranches of 25 basis points each |
CRR Effective Dates | – 4.25% of Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) from December 14, 2024 |
– 4.00% of NDTL from December 28, 2024 | |
Previous Reference Notification | DOR.RET.REC.33/12.01.001/2022-23 dated May 04, 2022 |
The link to the aforesaid Circular is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/NT89F4D92410284144889D442DB87332875D.PDF
4. Interest Rates on Foreign Currency (Non-resident) Accounts (Banks) [FCNR(B)] Deposits
- Vide: RBI/2024-25/94/ DoR.SPE.REC.No.51/13.03.00/2024-2025
- Dated: December 06, 2024
Summary
To attract more foreign capital, the RBI has raised the interest rate ceilings on FCNR-B deposits and increased FCNR deposit rates. These measures aim to strengthen the rupee and enhance India’s appeal as an investment destination. Higher FCNR deposit rates are expected to attract foreign capital, bolstering the rupee and reducing external vulnerabilities.
The RBI decided to increase the interest rates ceiling on fresh FCNR(B) deposits raised by the banks with effect from December 06, 2024, as under:
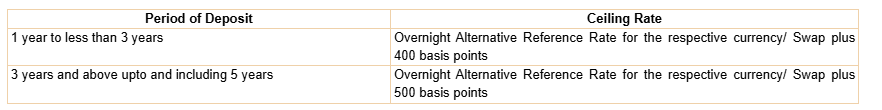
This adjustment reflects a significant increase over previous ceilings (previously 250 basis points for 1-3 years and 350 basis points for 3-5 years).
The link to the aforesaid Circular is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/NT90625ECB4FD4F04239BA69B10E311A9941.PDF
5. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) access for Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) through third-party applications
Currently, UPI payments from/to a bank account can be carried out using the UPI application of that bank or of any third-party application provider. However, UPI payments from/to a PPI can only be carried out using the mobile application provided by the PPI issuer.
As announced in the Statement on Development and Regulatory Policies dated April 05, 2024, it has been decided to enable UPI payments from/to full-KYC PPIs through third-party UPI applications. This will enable PPI holders to make/receive UPI payments through the mobile application of third-party UPI applications.
6. Reporting Platform for transactions undertaken to hedge price risk of gold
Banks must report gold derivatives transactions to the Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. starting February 1, 2025, and Reports should include all OTC transactions in domestic markets, IFSC, and abroad. This notification is aimed at improving the transparency and regulation of gold derivatives trading within the financial ecosystem.
1. Mandated Reporting:
– Banks must report all over-the-counter (OTC) transactions in gold derivatives by them and their customers to the Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) trade repository from February 01, 2025.
2. Reporting Requirements:
– All OTC transactions in gold derivatives must be reported by banks undertaken in domestic markets, International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), and outside India.
– Transactions must be reported before 12:00 noon of the following business day.
– Banks must also report all amendments and unwinding of transactions.
3. One-Time Data Submission:
– As a one-time measure, banks must report all matured and outstanding OTC transactions in gold derivatives from April 15, 2024, to February 28, 2025.
4. Quarterly Reporting:
– Banks are required to submit a quarterly report on transactions in gold derivatives undertaken by them and their customers at exchanges in IFSC and overseas, within ten days after each quarter, starting from the quarter ending December 31, 2024.
IMPORTANT PRESS RELEASES
1. Governor’s Statement: December 6, 2024
Here are the key points from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor’s statement dated December 6, 2024:
1. Economic Overview
– Global Challenges: Central banks face pressures due to geopolitical conflicts, financial market volatility, and complex economic shocks, impacting global economic stability.
– Indian Economy: Despite recent growth and inflation fluctuations, India is on a balanced path of progress, leveraging global economic trends as it undergoes transformational changes.
2. Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Decisions
– Policy Rates: The repo rate remains unchanged at 6.50%, with the standing deposit facility at 6.25% and the marginal standing facility and bank rate at 6.75%.
– Neutral Stance: The MPC continues to maintain a ‘neutral’ stance, focusing on balancing inflation control while supporting growth.
3. Economic Growth and Inflation
– Growth Projection: Real GDP growth for 2024-25 is projected at 6.6 percent, with Q3 at 6.8 percent; and Q4 at 7.2 percent. Real GDP growth for Q1:2025-26 is projected at 6.9 percent, and Q2 at 7.3 percent.
– Inflation Trends: Inflation surged above 6%, influenced by food prices, peaking at 9.7% in October. CPI inflation for 2024-25 is projected at 4.8 percent, with Q3 at 5.7 percent; and Q4 at 4.5 percent. CPI inflation for Q1:2025-26 is projected at 4.6 percent, and Q2 at 4.0 percent.
4. Key Economic Indicators
– Domestic Growth: A slowdown was noted in Q2 2024, largely from industrial deceleration. However, high-frequency indicators suggest recovery aided by festive demand and rural activity.
– External Sector: Merchandise exports surged by 17.2% in October 2024, while services exports grew substantially.
5. Financial Stability and Liquidity
– Liquidity Management: The banking system remains in surplus. To address potential liquidity tightening, the cash reserve ratio (CRR) for banks will be reduced to 4.0%.
– Rupee Stability: The Indian Rupee depreciated by 1.3% against the US dollar, with significant capital outflows noted in October and November.
6. Additional Measures
– Collaterals for Agriculture Loans: The limit for collateral-free agriculture loans increased from ₹1.6 lakh to ₹2 lakh.
– New Financial Initiatives: Introduction of new benchmarks for interest rate derivatives, expansion of foreign exchange platforms, and setting up an initiative for AI in financial regulations.
Key initiatives by the Reserve Bank of India:
1. Expansion of FX-Retail Platform
– Linkage with Bharat Connect: The FX-Retail platform, launched in 2019, will be linked with the NPCI’s Bharat Connect platform.
– User Benefits: This will enable transactions via bank and non-bank mobile apps, enhancing user experience and ensuring price fairness and transparency.
2. Introduction of Secured Overnight Rupee Rate (SORR)
– New Benchmark Proposal: The Reserve Bank aims to introduce SORR, which will be based on secured money market transactions, including overnight market repo and TREPS.
– Purpose: This is intended to develop the interest rate derivatives market and enhance the credibility of interest rate benchmarks.
3. ‘Connect 2 Regulate’ Initiative
– Open Regulation Program: A new program “Connect 2 Regulate” will be launched as part of RBI@90 events.
– Stakeholder Engagement: A dedicated section on the RBI website will allow stakeholders to provide input on specific regulatory topics.
4. Introduction of Podcast Facility
– Enhanced Communication: The Reserve Bank plans to introduce podcasts as part of its communication strategy to improve transparency and disseminate information widely.
5. Increase in Collateral-free Agriculture Loan Limit
– Revised Loan Limit: The limit for collateral-free agriculture loans will increase from ₹1.6 lakh to ₹2 lakh per borrower to address rising agricultural costs and enhance credit availability for small and marginal farmers.
6. Pre-sanctioned Credit Lines through UPI
– Inclusion of Small Finance Banks: Small Finance Banks will now be permitted to extend pre-sanctioned credit lines through UPI, in addition to Scheduled Commercial Banks.
– Financial Inclusion: This initiative aims to deepen financial inclusion and provide formal credit access, especially for new customers.
7. AI Framework for Responsible Enablement
– FREE-AI Initiative: A committee will be established to create a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI in the financial sector, addressing risks like algorithmic bias and data privacy.
8. AI Solutions to Identify Mule Bank Accounts
– MuleHunter.AI Development: An AI/ML-based solution, MuleHunter.AI has been developed to help banks identify and manage mule bank accounts, aiming to reduce digital fraud incidents.
These initiatives highlight the Reserve Bank of India’s commitment to enhancing the financial ecosystem, improving transparency, and fostering innovation through technology.
Link
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR1490B7B260EF5BAA403888462A4A6C6A5F7A.PDF
2. Shri Sanjay Malhotra takes over as RBI Governor
Shri Sanjay Malhotra, an Indian Administrative Service Officer of 1990 Batch Rajasthan Cadre, took over charge as the 26th Governor of the Reserve Bank of India for a period of three years effective December 11, 2024.
IMPORTANT PRESS RELEASES ON PENALTY LEVIED BY RBI
(CONSIDERED CASES WHERE PENALTY EXCEEDS 5 LAKHS)
1. RBI imposes monetary penalty on
- Panchkula Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. Haryana and
- Zila Sahkari Bank Ltd., Mirzapur
- The Ropar Central Co-operative Bank Ltd., Ropar, Punjab
- Kaithal Central Co-operative Bank Ltd., Haryana
Reason:
The bank had failed to transfer eligible unclaimed amounts to the Depositor Education and Awareness Fund within the prescribed time.
Amount
₹5.00 lakh (Rupees Five lakhs only) Each
The link to the aforesaid press release is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR1620D20A4DD3845E40AAB19996EBD60D7682.PDF
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR164215363841DDAA4E199BAB8EAED2B8FC99.PDF
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR16895E202A857D854285A4413F5038B40AEB.PDF
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR1808A554B8C8BA7F47F48230DE8442B6E06D.PDF
2. RBI imposes monetary penalty on Punjab Gramin Bank, Kapurthala, Punjab
Reason:
The bank had failed to transfer eligible unclaimed amounts to the Depositor Education and Awareness Fund within the prescribed time.
Amount
₹36.40 lakhs (Rupees Thirty-Six Lakhs Forty Thousand lakhs only)
The link to the aforesaid press release is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR1809FD79A1D1FD364C16A74B12CC4A4EA095.PDF
3. RBI imposes monetary penalty on SBPP Co-operative Bank Limited, Killa Pardi (Dist. Valsad)
Reason:
The bank had
- The bank was penalized for non-compliance with RBI directions related to ‘Income Recognition, Asset Classification, Provisioning, and Other Related Matters – UCBs’.
- The inspection revealed that the bank failed to classify loan accounts of certain borrowers as non-performing assets (NPAs).
Amount
₹15.00 lakh (Rupees Fifteen Lakhs only)
The link to the aforesaid press release is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR17100344A2F07F8C4042B7906E7D23CBF2FF.PDF
4. RBI imposes monetary penalty on Vaishya Sahakari Bank Limited, Mumbai, Maharashtra
Reason:
The bank had:
- Failure to deposit the prescribed amount in the MSE Refinance Fund due to a shortfall in the PSL target for FY 2022-23.
- Failure to deposit the prescribed amount in the MSE Refinance Fund maintained with SIDBI against the shortfall in achievement of the PSL target for FY 2022-23 within the prescribed time and even after the issuance of the cautionary letter, was sustained, warranting imposition of monetary penalty.
Amount
₹5.96 lakhs (Rupees Five lakh ninety-six thousand only)
The link to the aforesaid press release is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR17118C491D8A7EB347AF8B210EBEC26F719A.PDF
5. RBI imposes monetary penalty on IndusInd Bank Ltd
Reason:
The bank had:
- Non-complied with certain provisions of the ‘Reserve Bank of India (Interest Rate on Deposits) Directions, 2016’.
- RBI found, inter alia, that the charge pertaining to the opening of certain savings deposit accounts in the name of ineligible entities was sustained, warranting the imposition of a monetary penalty.
Amount
₹27.30 lakh (Rupees Twenty-Seven Lakh and Thirty Thousand only)
The link to the aforesaid press release is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR1753500E47EA13E14315A3B0577EDE79764B.PDF
6. RBI imposes monetary penalty on Manappuram Finance Limited
Reason:
RBI found that the following charges against the company were sustained, warranting the imposition of monetary penalty:
- It failed to undertake verification of PAN of customersfrom the verification facility of the issuing authority at the time of customer acceptance; and
- It allotted multiple identification codes to certain customers instead of a Unique Customer Identification Code (UCIC) for each customer.
Amount
₹20.00 lakh (Rupees Twenty Lakh only)
The link to the aforesaid press release is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR17545AE9E56240AA4446BC3027ECC0B58D5A.PDF
7. RBI imposes monetary penalty on SBPP Co-operative Bank Limited, Killa Pardi (Dist. Valsad)
Reason:
The bank had
- sanctioned fresh loans and advances carrying risk weights of more than 100% in violation of the directions issued under SAF; and
- sanctioned loans to nominal members in excess of the prescribed regulatory limit.
Amount
₹5.00 lakh (Rupees Five Lakhs only)
The link to the aforesaid press release is as follows:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR181369FAA997320B41EAB6BD9C10BB28A3AE.PDF
